|
SERPENTINITE #1 Serpentinite - Other specific examples: #1 | #2 | #3 | #4  Detail of this specimen
Detail of this specimen
Return to: Alphabetical Listing Basic Key Advanced Key |
|||
Composition
|
Description
A nondescript rock with a dark green to yellow-green color, often streaked or shot through with veins of other colors. Rock tends to be soft (H 3-5), and have a greasy or silky feel, especially on smooth flat surfaces; cut surfaces have a highly polished- waxed slickness to them. Luster tends to be dull or waxy. Once one becomes familiar with the rock it is distinctive and easy to recognize, but it is the "feel" of it that is most indicative. |
||
Tectonic Association
Serpentine forms from the alteration of ultramafic igneous rocks under low grade metamorphic conditions in the presence of lots of water so any circumstances that provide these conditions will result in serpentinite. Aside from these conditions there is no specific tectonic association associated with serpentinite.
|
Type of Metamorphism
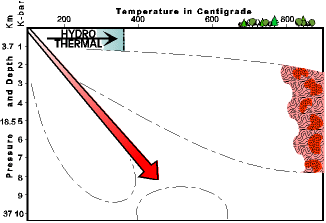 |
||